Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness. However, several other conditions mimic its symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. Understanding the key differences between RA and these conditions can help ensure proper treatment.
1. Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signs and Symptoms
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the cartilage. Unlike RA, which is an autoimmune condition, OA results from wear and tear over time. Symptoms include:
- Joint stiffness (worse after inactivity)
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Bone spurs formation
- Asymmetrical joint involvement
Key Differences
- OA affects larger weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips, while RA commonly targets smaller joints in the hands and feet.
- Morning stiffness in OA lasts less than 30 minutes, whereas RA stiffness persists for over an hour.
2. Lupus and Its Overlapping Symptoms with RA
Signs and Symptoms
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is another autoimmune disease that shares symptoms with RA, including:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Fatigue and fever
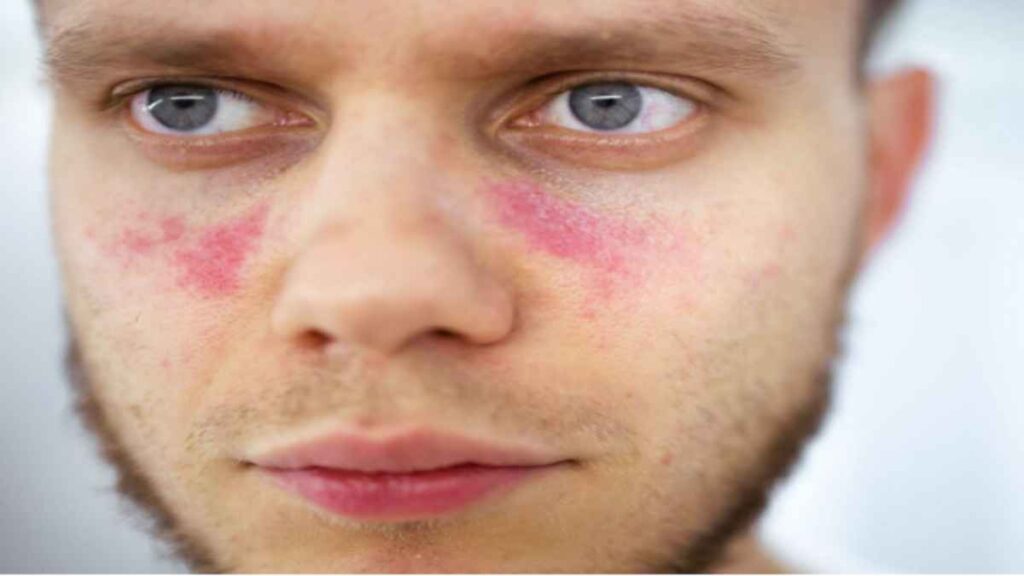
- Skin rashes (butterfly rash on the face)
- Organ involvement (kidneys, heart, lungs)
Key Differences
- Lupus affects multiple organs beyond the joints.
- RA primarily leads to joint deformity over time, while lupus may cause systemic damage.
- A positive ANA (antinuclear antibody) test is more common in lupus patients.
3. Psoriatic Arthritis: A Condition Similar to RA
Signs and Symptoms
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory arthritis linked to psoriasis. Symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Skin plaques with silvery scales
- Nail changes (pitting and ridging)
- Dactylitis (sausage fingers and toes)
Key Differences
- RA affects joints symmetrically, while PsA may cause asymmetric inflammation.
- PsA is often accompanied by skin issues, which are absent in RA.
4. Gout and Its Resemblance to RA
Signs and Symptoms
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup, leading to:
- Sudden, intense joint pain (often in the big toe)
- Redness and warmth in affected areas
- Tophi (uric acid crystal deposits)
Key Differences
- Gout attacks are episodic, while RA symptoms are chronic.
- RA affects multiple joints symmetrically, while gout typically impacts one joint at a time.
5. Fibromyalgia: A Commonly Confused Condition
Signs and Symptoms
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by:
- Widespread muscle pain and tenderness
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Cognitive issues (“fibro fog”)
Key Differences
- RA involves inflammation, while fibromyalgia does not.
- Joint damage occurs in RA but is absent in fibromyalgia.
6. Lyme Disease and RA Similarities
Signs and Symptoms
Lyme disease, caused by a bacterial infection from tick bites, can mimic RA with symptoms like:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Flu-like symptoms
- Neurological problems
Key Differences
- Lyme disease has a distinctive bull’s-eye rash.
- Antibiotics can treat Lyme disease, whereas RA requires immunosuppressive therapy.
7. Reactive Arthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signs and Symptoms
Reactive arthritis is an inflammatory condition that develops after an infection. Symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Eye inflammation (conjunctivitis)
- Urinary tract symptoms
Key Differences
- Reactive arthritis is triggered by an infection.
- It often resolves within months, unlike RA, which is chronic.
8. Ankylosing Spondylitis and RA: Similarities and Differences
Signs and Symptoms
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine. Symptoms include:
- Chronic back pain and stiffness
- Limited spinal mobility
- Postural changes
Key Differences
- RA mainly affects peripheral joints, whereas AS impacts the spine.
- AS is more common in young men.
9. Sarcoidosis: A Rare Autoimmune Condition That Mimics RA
Signs and Symptoms
Sarcoidosis is a condition involving the growth of inflammatory cells. Symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Lung and eye involvement
- Enlarged lymph nodes
Key Differences
- RA primarily affects the joints, while sarcoidosis can impact multiple organs.
10. Benefits of Accurate Diagnosis
A precise diagnosis ensures appropriate treatment, preventing unnecessary medications and worsening symptoms. Early intervention helps preserve joint function and overall well-being.
11. Potential Side Effects of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis can lead to:
- Unnecessary treatments with harmful side effects
- Disease progression due to delayed care
- Emotional distress from incorrect health assessments
12. Customer Reviews on Diagnosis Experiences
Patients often report frustration due to delayed diagnosis. Many have seen multiple specialists before receiving the correct diagnosis, emphasizing the need for thorough testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How do doctors differentiate RA from other conditions? A: Doctors use blood tests (RF, anti-CCP, ANA), imaging (X-rays, MRI), and symptom analysis.
Q2: Can RA be mistaken for lupus? A: Yes, as both are autoimmune diseases, but lupus has additional organ involvement.
Q3: Is fibromyalgia a form of arthritis? A: No, fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder without inflammation or joint damage.
Q4: How long does it take to diagnose RA? A: Diagnosis may take months due to overlapping symptoms with other conditions.
Q5: Can a blood test confirm RA? A: Blood tests help, but no single test can confirm RA. Clinical evaluation is necessary.
By understanding conditions that mimic rheumatoid arthritis, patients and healthcare providers can work together for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Early intervention improves quality of life and prevents long-term joint damage.